Governance
Hyosung Risk Management
As the complexity of the business environment and society increases, so does the number of unanticipated risks and new business opportunities. To ensure sustainable growth, a system capable of preventing and managing risks in advance is necessary.
Acknowledging risk management as a crucial management activity, Hyosung has established a risk management system to minimize direct or indirect negative environmental and social impacts resulting from the company's business operations.
In order to respond to stakeholders' increased interest in non-financial risks and to fulfill our corporate social responsibilities, we also enhance the management of risks that may arise from non-financial perspectives, such as environmental and social factors, in addition to traditional financial risks.
Risk management system
Link Copy- Hyosung Corporation’s Board of Directors and ESG Management Promotion Committee review and approve major company-wide risks and management plans.
- In 2022, the ESG Management Promotion Committee established an enterprise-wide risk management plan and process.
- Relevant departments identify, assess, and respond to risks based on internal team-level policies. For critical risks, an internal protocol mandates reporting to the ESG Management Committee for appropriate action.
- Hyosung Corporation transparently discloses key financial and non-financial risks in its Sustainability Report.
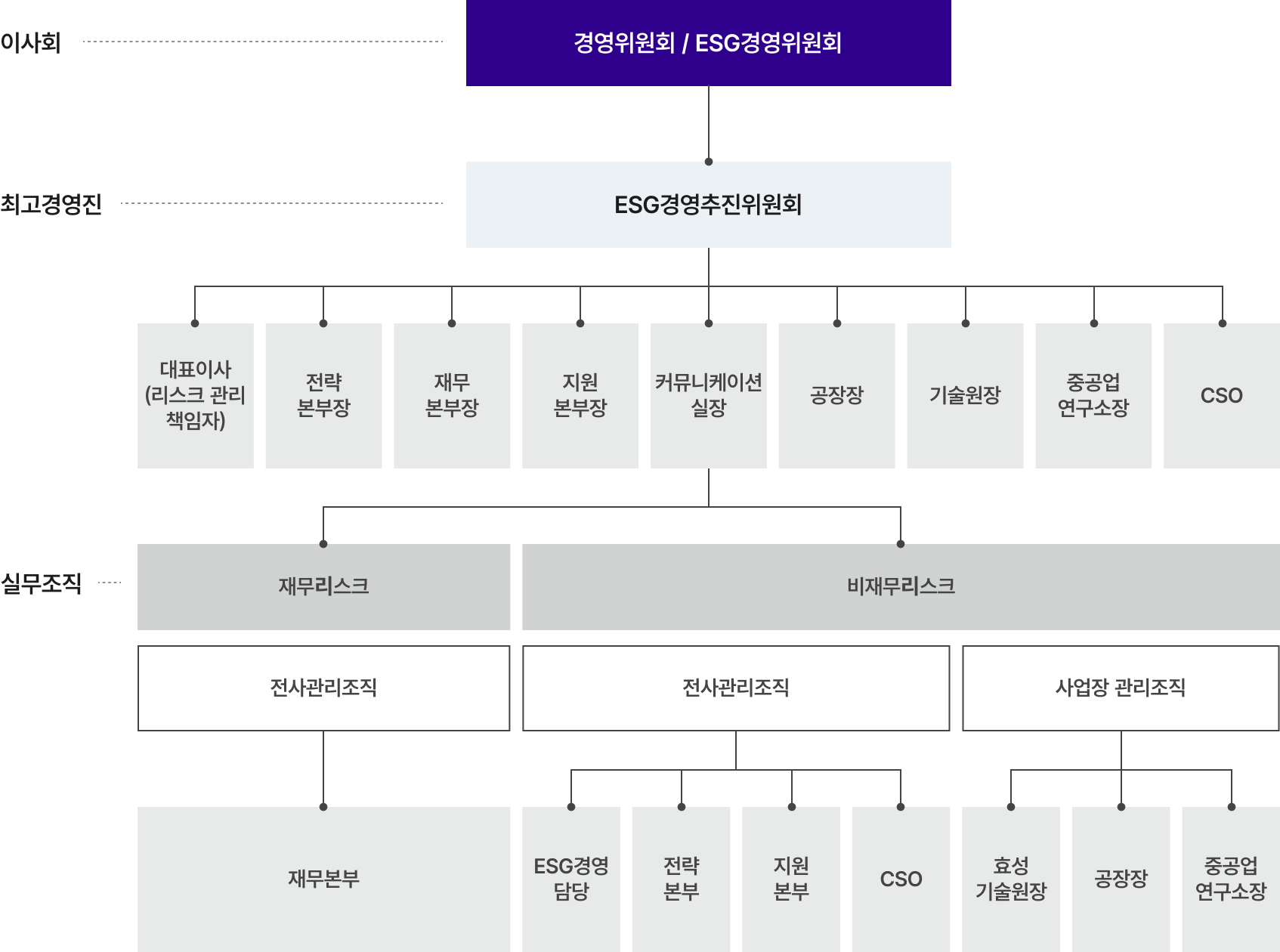
Risk Management Organization
Hyosung will manage risk issues and discuss key risks and responses at the board's management committee and ESG management committee. In addition, the ESG Management Promotion Committee under the CEO shall serve as the Chairman and Risk Management Officer, and shall manage company-wide financial and non-financial risks with the Director of Strategy, Finance, Support, Communication, Factory, Technology, Research, and CSO.
Financial risk is supervised by the Finance Headquarters and periodically measures, assesses, and hedges financial risk through organic cooperation with business units in the headquarters and domestic and foreign subsidiaries.
Non-financial risk is managed by ESG management team, strategic headquarters, support headquarters, CSO-centered enterprise risk management organization, and business environment, safety, supply stability, orders, sites, and litigation risk response organization led by PU and factory managers.
- BoD
- Management Committee / ESG Management Committee
- Top Management
-
ESG Management Promotion Committee
- CEO (Risk Management Officer)
- Director of Strategy Division
- Director of Finance Division
- Director of Support Division
- Head of Communication Office
- Plant Manager
- Head of Hyosung R&DB Labs
- Head of Power & Industrial Systems R&D Center
- CSO
- Working-level Organization
-
- Financial risks
- Non-financial risks
- Company-wide management organization
- company-wide management organization
- Business site management organization
- Finance Division
- ESG Management
- Strategy Division
- Support Division
- CSO
- Head of Hyosung R&DB Labs
- Plant Manager
- Head of Power & Industrial Systems R&D Center
Risk management process
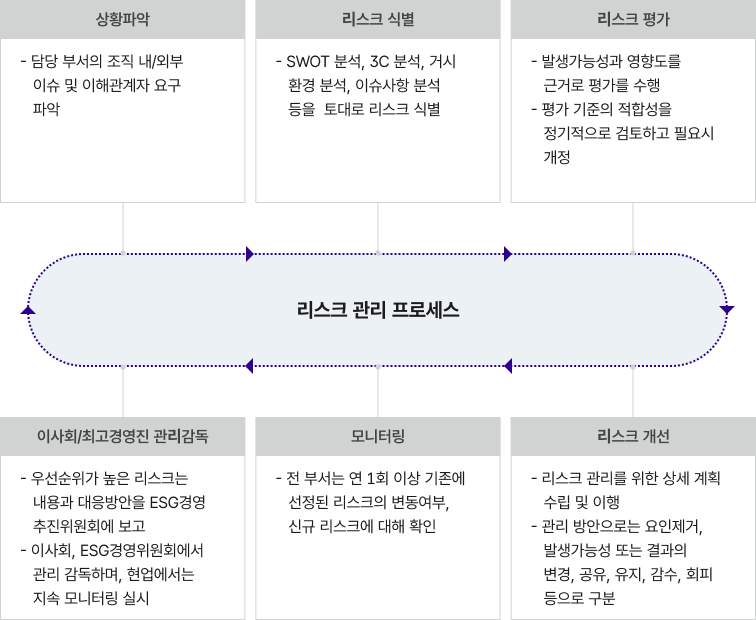
- Situation Assessment
-
Identify internal and external issues of the responsible departments and stakeholder demands
- Risk Identification
-
Risks are identified based on SWOT analysis, 3C analysis, macro-environmental analysis, and issue analysis
- Risk Evaluation
-
Evaluations are conducted based on likelihood and impact
The appropriateness of the evaluation criteria is reviewed regularly and revised as needed


- Supervision & Oversight from Board of Directors and Top Management
-
High-priority risks are reported to the ESG Management Committee along with their details and response plans
The Board of Directors and the ESG Management Committee oversee the process, while field departments continuously monitor these risks
- Monitoring
-
All departments check, at least once a year for changes in existing risks and identify any new risks
- Risk Improvement
-
Develop and implement detailed plans for risk management
Management strategies include elimination of risk factors, modification of likelihood or consequences, sharing, retention, acceptance, or avoidance
Management of risks in accordance with the major types
Financial Risks
| Category | Risk Details | Control Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Market |
Fluctuations in stock price, interest rates, and exchange rates |
Operate an internal accounting management system Minimize foreign exchange positions; clearly define measurement frequency, hedge duration, and hedge ratios in FX risk management policy |
| Credit |
Inability of customers or counterparties to fulfill contractual obligations |
Set and manage credit limits for trade receivables in accordance with internal credit management regulations Conduct credit assessments and manage collateral or recovery measures for investments and loans |
| Liquidity |
Risk of unexpected liquidity deterioration |
Regularly forecast future cash flows to maintain an appropriate level of cash reserves Establish agreements with financial institutions for emergency funding |
Non-Financial Risk – Business Continuity
| Category | Risk Details | Control Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain |
Delayed delivery due to failure in securing raw materials or ensuring production continuity |
Train for emergency response per scenario Conducts regular quality/environmental assessments of raw material suppliers according to IATF 16949, ISO 9001, and ISO 14001 Supports ESG capability-building for partners and conducts periodic assessments Operates the Bid Approval Committee (BAC) |
| Disasters & Safety |
Earthquakes, fires, or safety accidents at the workplace |
Operates a dedicated organization for safety risk management Forms emergency response teams; prepares manuals and recovery actions for each scenario Conducts regular joint public-private drills based on accident scenarios such as fires and explosions |
| Customer Safety |
Health and safety risks from harmful substances like heavy metals during product use; |
Conducts pre-inspects of hazardous substance leaching, including heavy metals, hazardous substances, and VOCs through component testing and analysis Discloses compliance with quality standards through ISIR reports, specifications, etc. Obtains safety certifications such as flame retardant certificates |
| Environmental |
Legal penalties/fines for environmental regulation violations |
Operates a dedicated team for environmental risk management Conducts regular risk assessments and prevention measures via environmental impact analysis Renews ISO 14001 certification and conducts internal audits Performs regular drills based on chemical or wastewater leakage scenarios |
Non-Financial Risks – Related to Management
| Category | Risk Details | Control Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change |
Risk of emissions-related regulations and physical risks leading to business transformation |
Operates a dedicated organization for climate change risk management, monitors relevant regulations, sets reduction targets, implements high-efficiency equipment, and fosters experts Monitors greenhouse gas emissions from Hyosung Corporation and its subsidiaries’ business sites, calculates product carbon emissions and implements reduction efforts Uses internal carbon pricing to guide business direction and investment decisions |
| Quality Management |
Risks due to changes in the 4M (man, machine, material, and method) Risks affecting continuous supply or delivery |
Evaluates the validity of 4M changes and monitors quality levels Manages through the non-conformance handling process Develops and conducts training for quality risk emergency scenarios |
| Human Rights |
Human rights violations and personnel management issues |
Conducts regular human rights impact assessments and follows up with improvement measures Establishes and implements a human rights policy and remedy manual for violations Conducts training on human rights protection and non-discrimination, and operates a reporting system |
| Information Security |
Risks of external cyber attacks, internal data leakage, and loss of information |
Identifies industrial and automotive floor carpets and carpet yarns (produced by Hyosung Corporation) as requiring information disclosure Conducts periodic vulnerability assessments and mitigation Prevents information leakage via Enterprise Content Management (ECM) and Information Security Center operations |
| Legal & Ethics |
Risks of unfavorable contracts, lawsuits, unfair trade practices, and corruption |
Prevents legal risks by adhering to contract review regulations and using standard contract templates; shares case studies to raise awareness Improves understanding through practical training in foreign exchange, patents, and contract management Conducts anti-corruption and ethics training covering the Anti-Graft Act, Subcontracting Act, and Fair Trade Act |
| Reputation |
Corporate image deterioration due to misinformation, negative communication, greenwashing, etc. |
Provides PR risk response training for new hires and promotees Conducts training on codes of conduct and response procedures for PR staff using case studies Promotes brand marketing and stakeholder communication through various channels Provides anti-greenwashing training for sales, PR, and marketing departments, and pre-reviews external publications by the compliance team |
| Information Disclosure |
Risk of legal violations, loss of customer trust, or product safety accidents due to insufficient product information |
Identifies industrial and automotive floor carpets and carpet yarns (produced by Hyosung Corporaion) as requiring information disclosure Provides details on manufacture date, lot number, material composition, handling instructions, and specifications through labeling Provides customers with technical documentation including inspection standards, test reports, and reliability test results |
